Japanese Journal of Health Economics and Policy,
Asian Pacific Journal of Health Economics and Policy
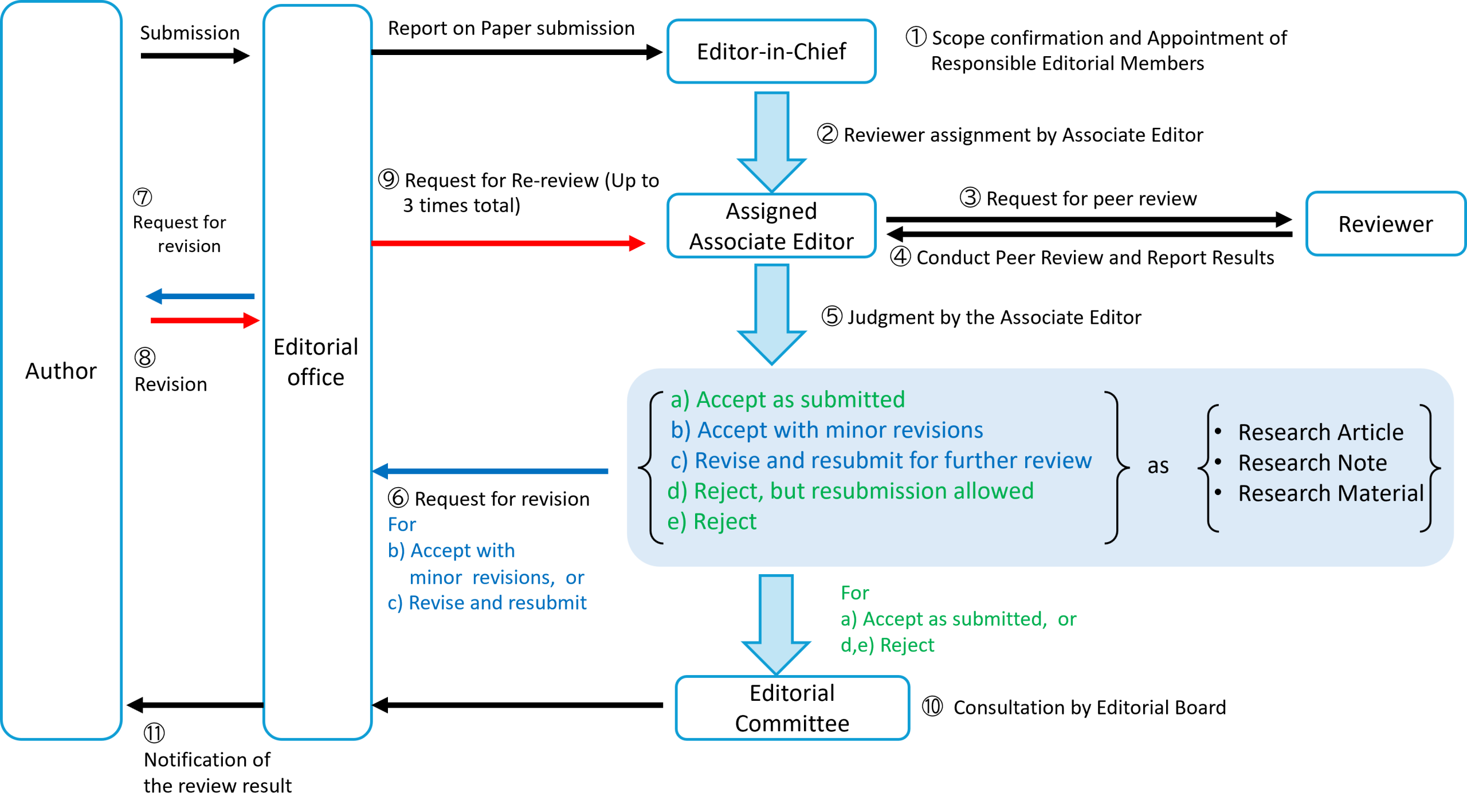
Peer Review Process
1) Initial Screening
The Editor-in-Chief will first determine whether a submitted manuscript falls within the scope of the journal (health economics and health policy) and meets the required academic standards. An Associate Editor will then be appointed to oversee the review process.
2) Reviewer Assignment
The assigned Associate Editor will invite one reviewer from outside the Editorial Committee. During this process, reviewer identities are kept anonymous from authors (single-blind review).
3) Conflict of Interest
Reviewers are required to confirm that they have no conflict of interest with respect to the manuscript. Any potential conflict must be reported promptly to the Editorial Office.
4) Review Procedure
The reviewer will assess the manuscript in accordance with the article type indicated by the author. The review will be conducted jointly by the reviewer and the assigned Associate Editor.
5) Review Outcomes
Reviewers are asked to recommend one of the following outcomes, and submit their report via the Editorial Office:
a) Accept as submitted
b) Accept subject to minor revision
c) Revise and resubmit for further review
d) Reject, with resubmission permitted after substantial revision
e) Reject
6) Editorial Decision
The Editorial Committee will make the final publication decision, with due consideration for the reviewer’s recommendation.
7) Notification of Authors
If the outcome is “b) Accept subject to minor revision” or “c) Revise and resubmit”, the Editorial Office will notify the author and request revisions.
8) Author Response
Authors requested to revise their manuscript are expected to respond to each point raised in the “Review Report” and “Reviewer Comments.” A revised manuscript, together with a detailed point-by-point response, must be submitted by the specified deadline.
9) Review Rounds
The review process is limited to a maximum of three rounds (initial review, first revision review, and second revision review). The reviewer’s recommendation at the third round will be considered final, and the Editorial Committee will then make its overall decision. (Minor editorial corrections are not included in this count.)
10) Final Decision
The Editorial Committee will issue the final decision on acceptance or rejection, and the Editorial Office will notify the author accordingly.
【Fig. Peer Review Flow】
Evaluation Criteria for Manuscripts
1) Clarity of the Research Question
The manuscript should clearly define its main research subject and objectives.
2) Originality of the Contribution
The work should demonstrate novelty, including new perspectives, methods, or use of data that advance the field.
3) Validity of the Conclusions
Conclusions must be logically supported by the analysis and evidence provided, with appropriate acknowledgement of limitations.
4) Adequacy of the Literature Review
Relevant literature should be sufficiently reviewed and appropriately cited, demonstrating awareness of current scholarship.
5) Clarity, Conciseness, and Accuracy of Writing
Writing should be clear, concise, and accurate. When numerous language errors or typographical mistakes are present, reviewers need only provide one representative example.
6) Appropriateness of Figures and Tables
Figures and tables should be necessary, correctly presented, and contribute meaningfully to the understanding of the manuscript.
7) Need for Substantial Revision
Reviewers should assess whether significant rewriting is required to meet publication standards.
8) Accuracy of English Expression
The manuscript should not contain expressions that could lead to misunderstanding or misinterpretation.
Instructions and Considerations for Reviewers
1) Confirmation of Non-Involvement
Reviewers must confirm that they have no direct involvement with the manuscript or conflicts of interest. If any involvement exists, the reviewer should notify the Editorial Office immediately.
2) Content of the Review
Reviewers are asked to provide their recommendation regarding publication, comments to the Associate Editor, and detailed reviewer comments for the authors.
3) Recommendation for Publication
Reviewers should first confirm the intended article type and then select one of the following recommendations:
● Accept as submitted
● Accept subject to minor revisions
● Revise and resubmit for further review
● Reject, but resubmission permitted after substantial revision
● Reject
Guidelines for recommendations:
i. For manuscripts recommended for rejection, reviewers should provide detailed comments explaining the specific reasons for rejection.
ii. For manuscripts recommended as “Accept subject to minor revision,” “Revise and resubmit,” or “Reject but resubmission permitted,” reviewers should identify specific concerns or issues and, when feasible, suggest concrete ways to address them.
Reviewers should assess whether the conclusions are logically supported by the results and methodology. Personal agreement or disagreement with the authors’ theoretical stance, policy positions, or conclusions should not influence the review. The evaluation should focus on methodological rigor, logical consistency, and evidence quality rather than ideological alignment.
4) Adequacy of the Literature Review
Reviewer comments should include:
i. Overall Assessment: Evaluation of novelty, methodological rigor, validity of conclusions, and adequacy of the literature review.
ii. Section-Specific Comments: Specific questions or issues should be identified with precise references to manuscript sections, and constructive suggestions for improvement should be provided when possible.
iii. Language and Presentation: If there are numerous language or typographical errors, it is sufficient to indicate one representative example.
5) Clarity, Conciseness, and Accuracy of Writing
When reviewing manuscripts submitted primarily as research data or materials, reviewers should focus on factual accuracy and potential misunderstandings. For such submissions, reviewers should generally consider the manuscript favorably for publication when the data or materials provide valuable information for future research, even if the analysis or interpretation may be limited.
6) Appropriateness of Figures and Tables
Reviewer comments will be shared with authors without revealing the names of the reviewers or the handling Associate Editor.
7) Need for Substantial Revision
If a manuscript is resubmitted following a recommendation of “Accept subject to minor revision” or “Revise and resubmit,” the original reviewer may be asked to review it again. In such cases, the reviewer should focus primarily on the issues they raised previously and avoid imposing new requirements on the author unless significant new concerns emerge.
8) Accuracy of English Expression
The Editorial Committee makes the final decision on publication, and reviewers will be informed of the outcome.
Article Type Instructions
● Research Article
Research articles present theoretical or empirical research findings and must demonstrate clear originality and contribution to the field.. No specific format is mandated; however, for empirical studies, the objectives, methods, results, and discussion should be clearly structured and described.
● Research Note
Research notes follow a format similar to research articles but present work that is original yet does not fully meet the criteria of a research article. This category may include studies with certain limitations in methodology, data scope, or generalizability. For example, an empirical study conducted at a single institution may be considered a research note if its broader applicability is limited, while still providing valuable insights.
● Research Material
Research materials include distinctive datasets, surveys, experimental designs, or reports on methodological improvements that provide information useful for future research. These submissions focus on the quality and potential utility of the data or methods rather than comprehensive analysis. The format may be similar to that of a research article or may follow an alternative structure appropriate to the material presented.
● Other
Other types of submissions recognized by the Editorial Committee include invited articles, letters to the editor, and information related to the activities of the Japan Health Economics Association or the Institute of Health Economics and Policy (such as conference announcements, policy updates, or institutional reports).
Editorial Committee of the Japan Health Economics Association
September 2025
